Food of a parrot plays a crucial role in maintaining their health and well-being. Understanding their nutritional needs, food types, and feeding habits is essential for parrot owners. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of parrot nutrition, providing valuable insights into the diverse and fascinating world of these captivating birds.
Nutritional Requirements
Parrots, as captivating and intelligent creatures, demand a well-rounded diet to thrive. Their nutritional needs encompass a spectrum of essential nutrients, including:
- Carbohydrates: Fuel for energy
- Proteins: Building blocks for tissues and organs
- Fats: Energy storage and hormone production
- Vitamins: Essential for metabolic processes
- Minerals: Skeletal and muscular health
The specific proportions of these nutrients vary based on parrot species, age, and activity level. The table below provides recommended daily nutrient intake for different parrot species:
| Nutrient | African Grey Parrot | Cockatoo | Macaw |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 50-60% | 55-65% | 60-70% |
| Proteins | 15-20% | 18-22% | 20-25% |
| Fats | 10-15% | 12-16% | 14-18% |
| Vitamins | 2-3% | 2.5-3.5% | 3-4% |
| Minerals | 1-2% | 1.5-2.5% | 2-3% |
Maintaining a balanced diet is paramount for parrot health. Deficiencies or excesses of any nutrient can lead to a cascade of health issues, ranging from feather plucking to reproductive problems. By providing a diverse and nutrient-rich diet, we ensure our feathered companions live long, healthy, and vibrant lives.
Food Types

Parrots have diverse dietary needs that vary depending on their species, size, and age. Understanding the different types of food they can consume is essential for providing a balanced and nutritious diet.
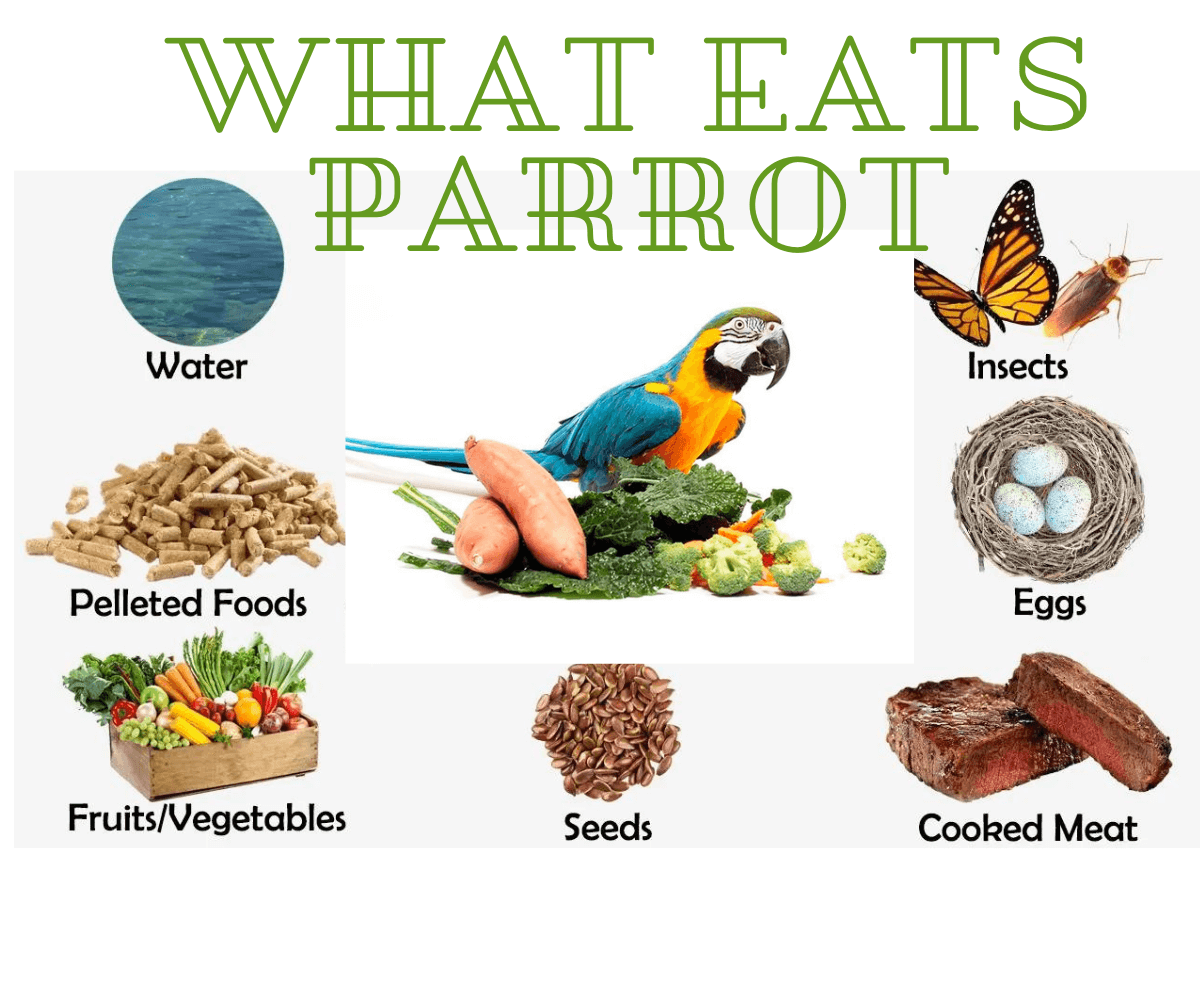
Parrot foods can be broadly categorized into three main types: seeds, pellets, and fresh foods.
Seeds
- Nutritional Value:Seeds are high in fat, carbohydrates, and protein, providing essential energy and nutrients.
- Benefits:Seeds are a natural food source for parrots, providing a sense of foraging and enrichment.
- Caution:Seeds should be offered in moderation due to their high fat content, which can lead to obesity if overconsumed.
Pellets
- Nutritional Value:Pellets are formulated to provide a complete and balanced diet, containing a blend of essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients.
- Benefits:Pellets ensure parrots receive all the necessary nutrients they need, reducing the risk of dietary deficiencies.
- Caution:Some parrots may be reluctant to eat pellets, especially if they are accustomed to a seed-based diet.
Fresh Foods
- Nutritional Value:Fresh foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and leafy greens, provide essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber.
- Benefits:Fresh foods promote digestive health, hydration, and overall well-being in parrots.
- Caution:Some fresh foods, such as avocados and chocolate, are toxic to parrots and should be avoided.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
| Food Type | Fat | Carbohydrates | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seeds | High | Moderate | High |
| Pellets | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Fresh Foods | Low | Low | Low |
Food Preparation
Preparing parrot food safely is essential for their well-being. Here are some tips to ensure your feathered friend enjoys healthy and nutritious meals:
Hygiene
Maintaining hygiene when handling parrot food is crucial to prevent contamination and the spread of bacteria. Wash your hands thoroughly before preparing their food, and use clean utensils and containers. Disinfect surfaces and equipment regularly to minimize the risk of cross-contamination.
Homemade Parrot Food, Food of a parrot
Making homemade parrot food allows you to control the ingredients and ensure their freshness. However, it’s important to follow recipes carefully and ensure the food is nutritionally balanced. Store homemade parrot food in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 3 days, or freeze it for longer storage.
Feeding Habits
In the wild, parrots are predominantly frugivores, with a diet consisting mainly of fruits, nuts, seeds, and occasionally insects and small animals. Their natural feeding habits vary significantly depending on the species and habitat. For instance, some species like macaws specialize in consuming hard-shelled nuts, while others like lories primarily feed on nectar and pollen.
Importance of Dietary Variety
Providing a varied diet is crucial for captive parrots to prevent boredom and ensure their nutritional needs are met. A monotonous diet can lead to health problems and behavioral issues. Offering a wide range of food choices allows parrots to select items that they enjoy and provides essential nutrients.
Feeding Frequency

The optimal feeding frequency for parrots depends on several factors, including their age, size, and activity level. Younger parrots typically require more frequent feedings than older ones, and larger parrots generally need to eat more than smaller ones. Active parrots may also need to eat more often than less active ones.
Feeding Schedule
A general feeding schedule for parrots is as follows:
- Morning:Offer a fresh bowl of pellets or seeds.
- Midday:Provide a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Afternoon:Offer a small snack, such as a piece of fruit or a nut.
- Evening:Feed a final meal of pellets or seeds.
Consequences of Overfeeding and Underfeeding
Overfeeding can lead to obesity, which can cause a variety of health problems, including heart disease, liver disease, and arthritis. Underfeeding can also lead to health problems, such as malnutrition, weight loss, and lethargy.
Food Safety
Food safety is crucial for the well-being of parrots. Improper handling or storage of food can lead to contamination and illness. Understanding common food hazards and implementing preventive measures are essential to ensure the safety of your feathered companion.
Identifying Food Hazards
- Bacteria:Salmonella, E. coli, and Pseudomonas can cause gastrointestinal distress and other health issues.
- Fungi:Molds and yeasts can produce toxins that can be harmful to parrots.
- Pesticides and herbicides:Residues on fruits and vegetables can be toxic to parrots.
- Heavy metals:Lead and zinc from galvanized metal cages or contaminated water can cause serious health problems.
Preventing Food Contamination
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before feeding.
- Cook meat and eggs thoroughly to kill bacteria.
- Avoid feeding spoiled or moldy food.
- Store food in airtight containers to prevent contamination.
- Keep food and water dishes clean and disinfected.
Recognizing Signs of Foodborne Illness
- Diarrhea or vomiting
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Swelling or redness around the beak or eyes
- Difficulty breathing
If you suspect your parrot has foodborne illness, seek veterinary attention immediately.
Food Enrichment: Food Of A Parrot
Food enrichment is crucial for parrots’ mental and physical well-being. It stimulates their natural foraging instincts, promotes cognitive function, and prevents boredom.
To create enriching feeding experiences, offer a variety of foods in different textures, shapes, and colors. Hide food items in toys or puzzles to encourage foraging. Scatter seeds or nuts around the cage to mimic natural feeding behaviors.
Case Studies
- A study by the University of California, Davis found that parrots fed an enriched diet had significantly higher levels of cognitive function compared to those fed a standard diet.
- A program at the San Diego Zoo Safari Park successfully implemented food enrichment for parrots, resulting in reduced aggression and increased social interactions.
Food Allergies and Intolerances
Food allergies and intolerances can affect parrots just like they do humans. It’s important to be aware of the common food allergies and intolerances in parrots so that you can avoid feeding your bird foods that may cause a reaction.
Symptoms of food allergies and intolerances in parrots can include:
- Skin irritation
- Feather plucking
- Gastrointestinal upset
- Respiratory problems
If you think your parrot may have a food allergy or intolerance, it’s important to take them to a veterinarian for diagnosis. Your veterinarian will be able to perform tests to determine what foods your parrot is allergic to and recommend a course of treatment.
There is no cure for food allergies and intolerances, but they can be managed by avoiding the foods that cause a reaction. If your parrot has a food allergy, it’s important to read food labels carefully and avoid giving your bird any foods that contain the allergen.
You should also be aware of the foods that are cross-contaminated with the allergen, and avoid these foods as well.
Food and Behavior
Parrots are highly intelligent birds with complex behavioral patterns. Their diet plays a significant role in shaping their behavior, both positively and negatively.
Food can be used as a powerful tool in training parrots. By offering treats or favorite foods as rewards for desired behaviors, owners can reinforce positive actions and encourage their pets to learn new skills. Conversely, withholding food or offering less desirable foods can be used as a form of punishment for undesirable behaviors, helping to discourage them.
Using Food for Positive Reinforcement
- Identify preferred foods:Determine which foods your parrot enjoys the most and use them as rewards during training sessions.
- Establish clear criteria:Define the specific behaviors you want to reinforce and consistently reward your parrot when they exhibit those behaviors.
- Be timely and consistent:Offer rewards immediately after the desired behavior occurs and maintain consistency in your training approach.
- Avoid overfeeding:While food can be a valuable training tool, it’s important to avoid overfeeding your parrot, as this can lead to weight gain and other health problems.
Questions and Answers
What are the essential nutrients parrots need?
Parrots require a balanced diet rich in carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Key nutrients include vitamin A, vitamin E, calcium, and iodine.
How often should I feed my parrot?
Feeding frequency varies depending on the parrot’s age, size, and activity level. Generally, adult parrots should be fed twice a day, while younger parrots may require more frequent feedings.
What are some common food allergies in parrots?
Common food allergies in parrots include peanuts, avocados, chocolate, and dairy products. Symptoms of allergies can range from skin irritation to respiratory distress.
