Keep food hot – In the realm of culinary delights, preserving the warmth and savor of freshly prepared meals is an art form. Embark on a gastronomic adventure as we explore the multifaceted world of keeping food hot, unraveling traditional techniques and embracing modern innovations.
From age-old methods to cutting-edge technologies, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to keep your culinary creations tantalizingly warm, ensuring every bite is a symphony of flavors.
Methods to Keep Food Hot

Preserving the temperature of cooked food is essential for both safety and enjoyment. Various methods exist to keep food hot, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Factors to consider when selecting a method include the type of food, desired temperature, and available resources.
Traditional Methods
- Double Boiler:A double boiler consists of two pots, one placed inside the other. Water is added to the bottom pot, and the food is placed in the top pot. The water heats up and creates steam, which gently cooks and keeps the food hot without overcooking.
- Thermal Cooker:A thermal cooker is an insulated container that utilizes the principle of residual heat. Food is heated to the desired temperature and then placed inside the cooker. The insulation traps the heat, allowing the food to stay hot for several hours.
- Slow Cooker:A slow cooker is an electric appliance that cooks food at a low temperature for an extended period. The slow cooking process ensures that the food remains hot and tender throughout the cooking time.
Modern Methods
- Sous Vide:Sous vide is a cooking technique that involves vacuum-sealing food in a plastic bag and cooking it in a temperature-controlled water bath. This method allows for precise temperature control and prevents overcooking.
- Microwave:Microwaves can be used to reheat food quickly and evenly. However, they may not be suitable for all types of food, as they can cause uneven heating and drying.
- Electric Warming Tray:Electric warming trays are designed to keep food warm for serving. They are typically used in buffet settings or for keeping food hot at gatherings.
Types of Food Warmers
Food warmers are essential tools for keeping food at optimal temperatures for extended periods. They come in various types, each with unique features and applications. Choosing the right type of food warmer depends on factors such as capacity, temperature control, and energy efficiency.
The following table provides an overview of different types of food warmers, their features, benefits, and applications:
| Type | Features | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chafing Dishes | – Portable
|
– Versatile and convenient
|
|
| Slow Cookers | – Electric appliances
|
– Energy-efficient
|
|
| Food Warmers | – Electric or gas-powered appliances
|
– Convenient for restaurants, cafeterias, and foodservice operations
|
|
| Soup Kettles | – Large, insulated containers
|
– Ideal for soup kitchens, cafeterias, and large-scale catering events
|
|
| Infrared Food Warmers | – Use infrared technology to heat food evenly
|
– Energy-efficient
|
When selecting a food warmer, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Capacity:The capacity of the food warmer should be appropriate for the amount of food you need to keep warm.
- Temperature Control:The food warmer should have adjustable temperature settings to ensure that the food is kept at the optimal temperature.
- Energy Efficiency:Energy-efficient food warmers can help reduce operating costs.
- Durability:The food warmer should be made of durable materials that can withstand regular use and cleaning.
- Safety:The food warmer should have safety features such as automatic shut-off and temperature monitoring.
Best Practices for Keeping Food Hot: Keep Food Hot
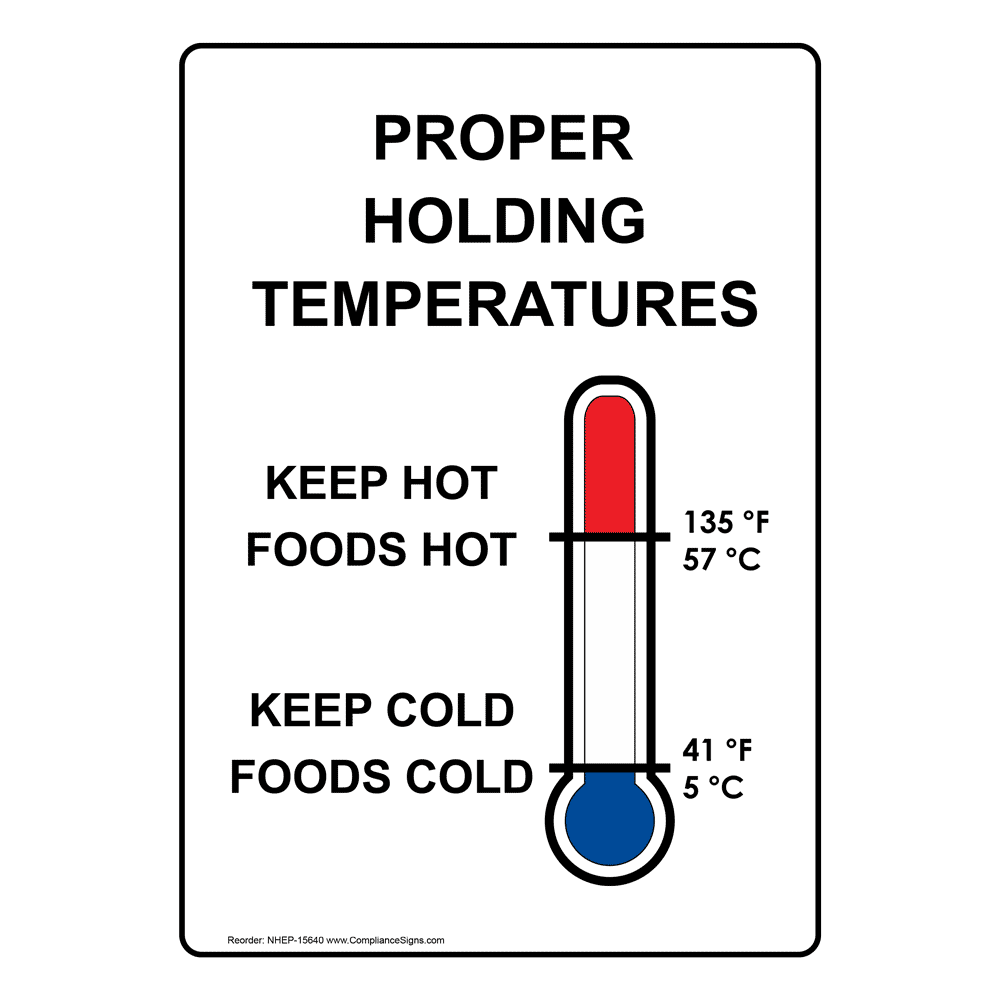
Ensuring food remains hot and safe to consume requires adherence to specific best practices. These guidelines involve proper storage, handling, and reheating techniques, each playing a crucial role in maintaining food temperature, preventing spoilage, and preserving food safety.
Proper Storage
Adequate storage is essential to maintain food temperature and prevent spoilage. Store hot food in insulated containers or warming trays designed to retain heat effectively. Avoid storing hot food in the refrigerator or freezer, as rapid cooling can create a favorable environment for bacterial growth.
Proper Handling
Proper handling practices minimize contamination and ensure food safety. Use clean utensils when serving hot food, and avoid cross-contamination by keeping raw and cooked foods separate. Monitor food temperatures regularly using a food thermometer to ensure they remain within the safe temperature zone (above 145°F or 63°C).
Proper Reheating
Reheating food safely is crucial to eliminate potential bacteria growth. Reheat food to an internal temperature of 165°F or 74°C, ensuring it is heated evenly throughout. Avoid reheating food multiple times, as this can increase the risk of contamination and spoilage.
Innovative Solutions for Keeping Food Hot

As technology advances, so do the methods we use to keep food hot. Innovative solutions are emerging to address the challenges of maintaining food temperature while ensuring safety and convenience.
Insulated Containers
Insulated containers, such as vacuum flasks and thermal bags, utilize materials with low thermal conductivity to create a barrier against heat transfer. They trap heat inside, keeping food warm for extended periods.
Self-Heating Devices
Self-heating devices offer a convenient solution for warming food on the go. These devices use exothermic chemical reactions or electrical heating elements to generate heat and raise the temperature of food.
Smart Appliances
Smart appliances, such as warming drawers and slow cookers, provide precise temperature control and extended heating capabilities. They allow for pre-programming of cooking and warming cycles, ensuring food is ready at the desired time and temperature.
Limitations and Challenges
While innovative solutions offer advantages, they also have limitations. Insulated containers can be bulky and may not maintain heat for as long as desired. Self-heating devices require additional fuel or power sources and may not be suitable for all situations.
Smart appliances can be expensive and require specialized knowledge for operation.
Considerations for Different Food Types
Keeping different types of food hot requires specific considerations to maintain their optimal temperature, texture, and quality. Understanding the unique characteristics of each food type is crucial to prevent overcooking, drying out, or compromising their flavor.
Meats
- Whole cuts:Roast meats, such as beef, pork, or chicken, should be kept at a temperature of 145°F (63°C) to ensure food safety and maintain tenderness.
- Ground meats:Hamburgers, meatballs, and sausage must be cooked to an internal temperature of 160°F (71°C) to eliminate bacteria and prevent undercooking.
- Poultry:Chicken, turkey, and duck should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to ensure thorough cooking and prevent foodborne illnesses.
Vegetables, Keep food hot
- Leafy greens:Spinach, lettuce, and arugula should be kept at a lower temperature, around 120°F (49°C), to prevent wilting and maintain their crisp texture.
- Root vegetables:Carrots, potatoes, and beets can withstand higher temperatures, up to 160°F (71°C), without losing their texture or flavor.
- Vegetables with high moisture content:Zucchini, tomatoes, and mushrooms should be kept at a moderate temperature, around 140°F (60°C), to prevent overcooking and preserve their delicate flavors.
Sauces
- Cream-based sauces:Alfredo, béchamel, and hollandaise sauces should be kept warm but not boiling, as high temperatures can cause them to curdle or separate.
- Tomato-based sauces:Marinara, arrabiata, and puttanesca sauces can be kept at a simmering temperature of around 180°F (82°C) to enhance their flavors and prevent burning.
- Gravies:Pan drippings, stock-based gravies, and roux-based gravies should be kept at a temperature of around 160°F (71°C) to maintain their consistency and prevent thickening excessively.
Desserts
- Cakes:Cakes should be kept at room temperature, around 70°F (21°C), to prevent them from drying out or becoming stale.
- Pies:Fruit pies can be kept at a slightly higher temperature, around 120°F (49°C), to maintain their crust’s crispiness and prevent the filling from becoming soggy.
- Custards:Crème brûlée, panna cotta, and custards should be kept at a temperature of around 140°F (60°C) to prevent curdling or separating.
Questions and Answers
Can I keep food hot in a slow cooker?
Yes, slow cookers are excellent for keeping food hot for extended periods. They maintain a low and steady temperature, ensuring your dishes remain warm and ready to serve.
What is the best way to keep fried food crispy?
To maintain the crispiness of fried food, place it on a wire rack set over a baking sheet. This allows air to circulate around the food, preventing it from becoming soggy.
How long can I safely keep food hot?
According to food safety guidelines, hot food should be kept at a temperature of 145°F (63°C) or above. It’s recommended to consume or refrigerate leftovers within 2 hours of cooking to prevent bacterial growth.
